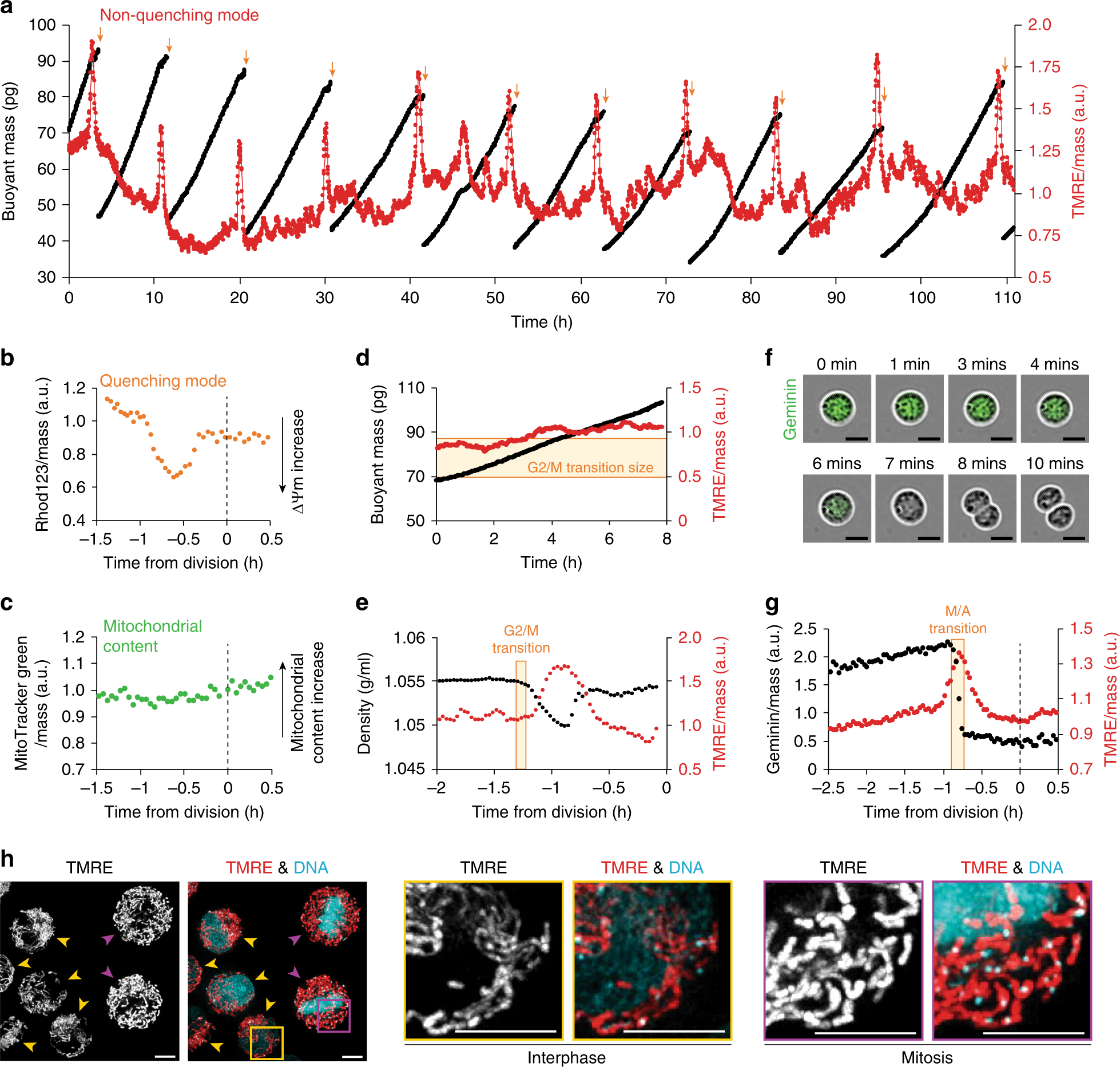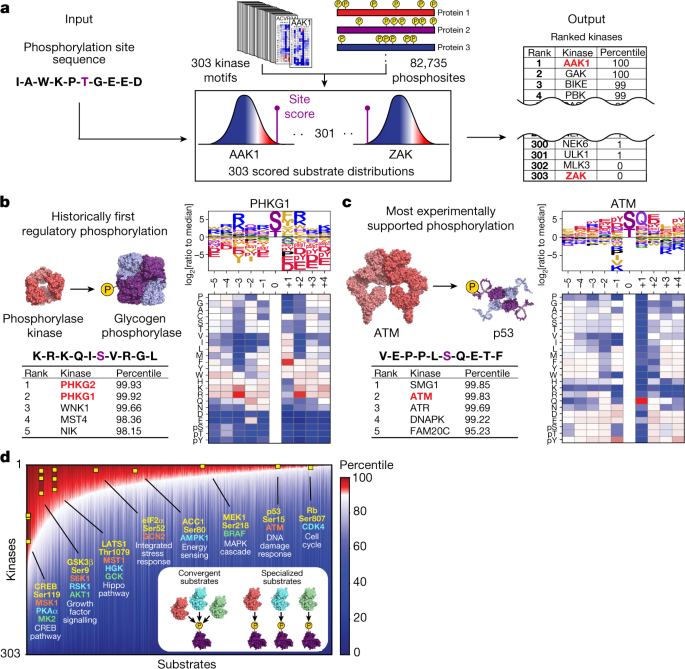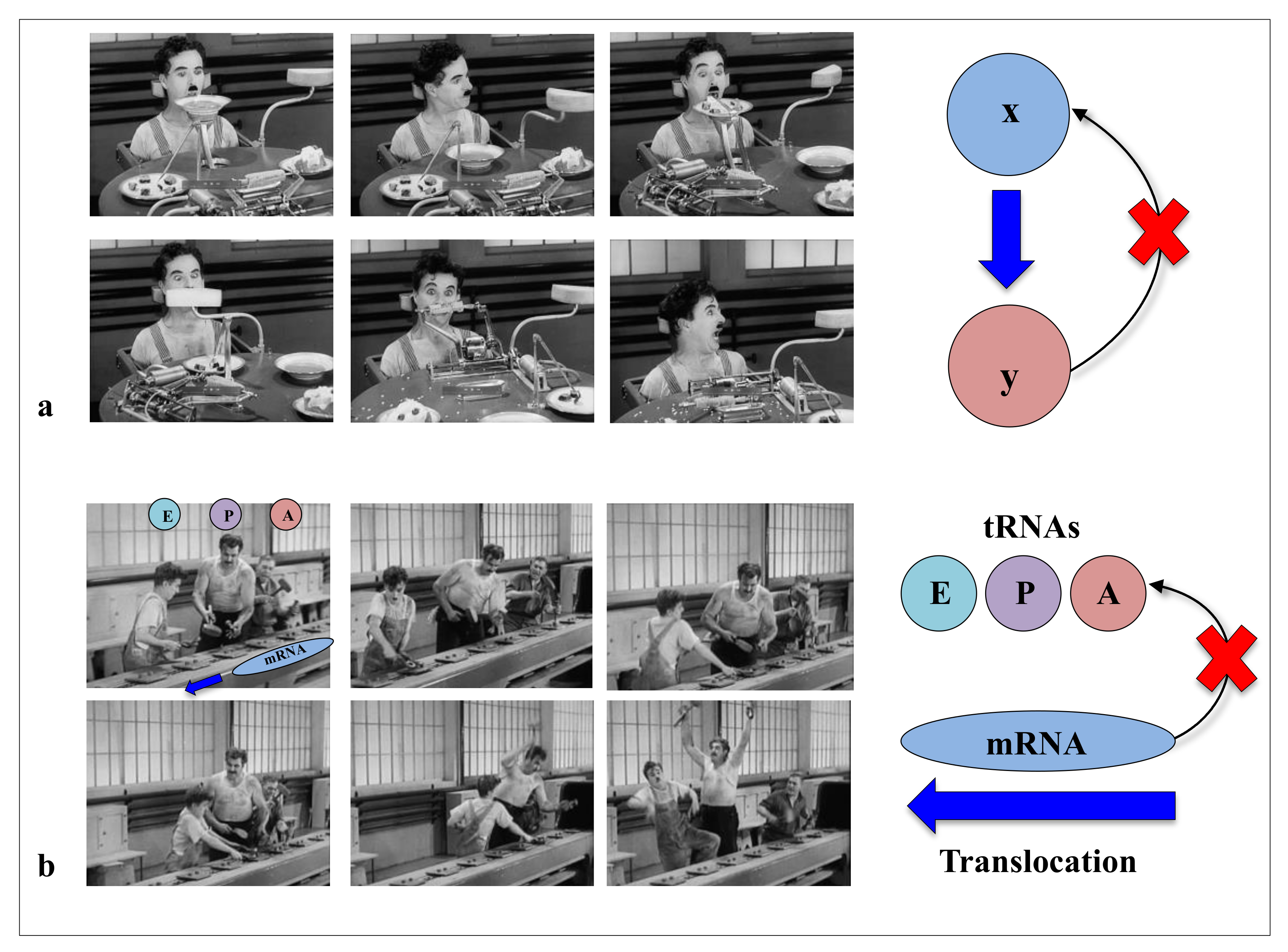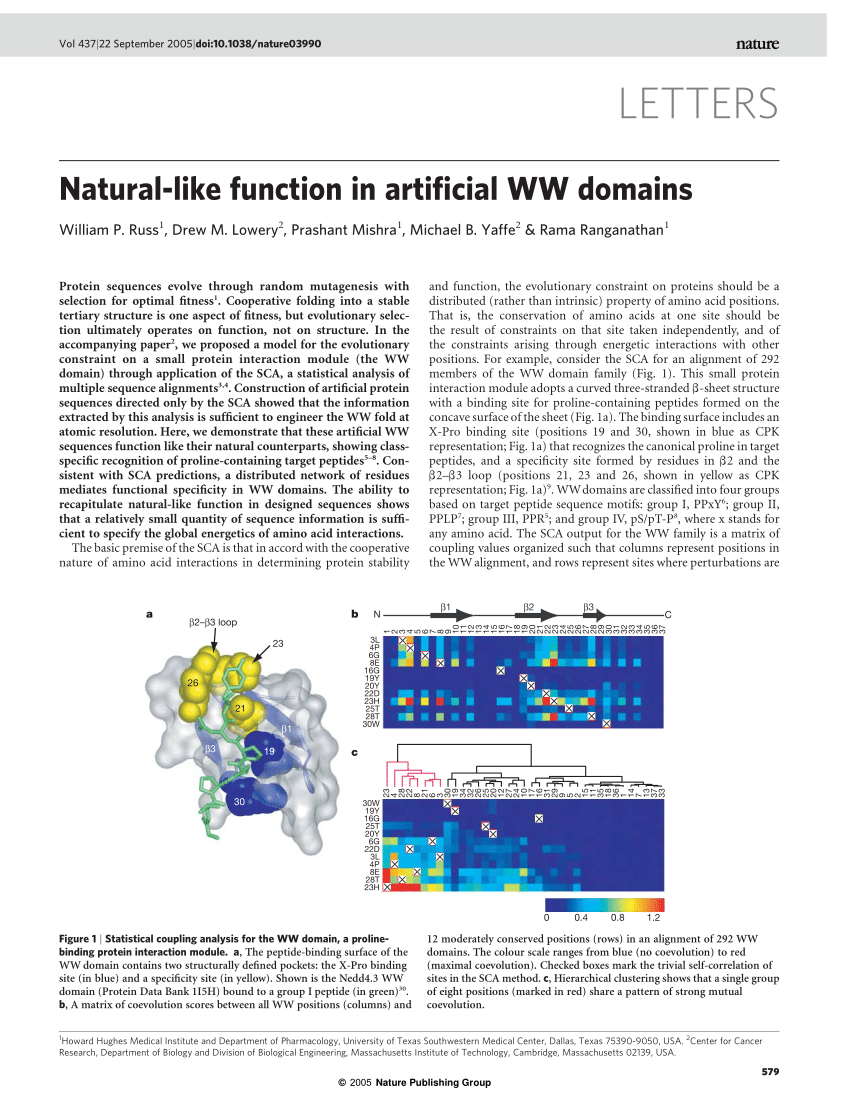
Biomolecules | Free Full-Text | Coordination of RNA Processing Regulation by Signal Transduction Pathways

Membrane Permeable Cyclic Peptidyl Inhibitors against Human Peptidylprolyl Isomerase Pin1 | Journal of Medicinal Chemistry
Helicase Q promotes homology-driven DNA double-strand break repair and prevents tandem duplications | Nature Communications

Theoretical Study of Cisplatin Binding to Purine Bases: Why Does Cisplatin Prefer Guanine over Adenine? | Journal of the American Chemical Society
TNK1 is a ubiquitin-binding and 14-3-3-regulated kinase that can be targeted to block tumor growth | Nature Communications
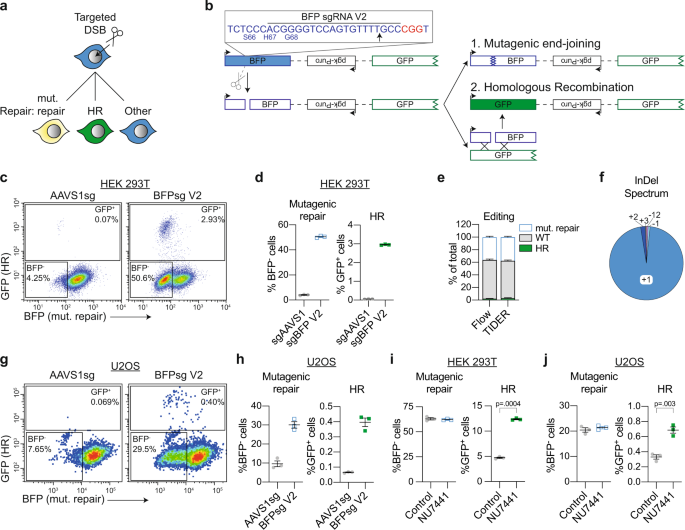
Multi-pathway DNA-repair reporters reveal competition between end-joining, single-strand annealing and homologous recombination at Cas9-induced DNA double-strand breaks | Nature Communications

Phospho-Ser/Thr-binding domains: navigating the cell cycle and DNA damage response | Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology
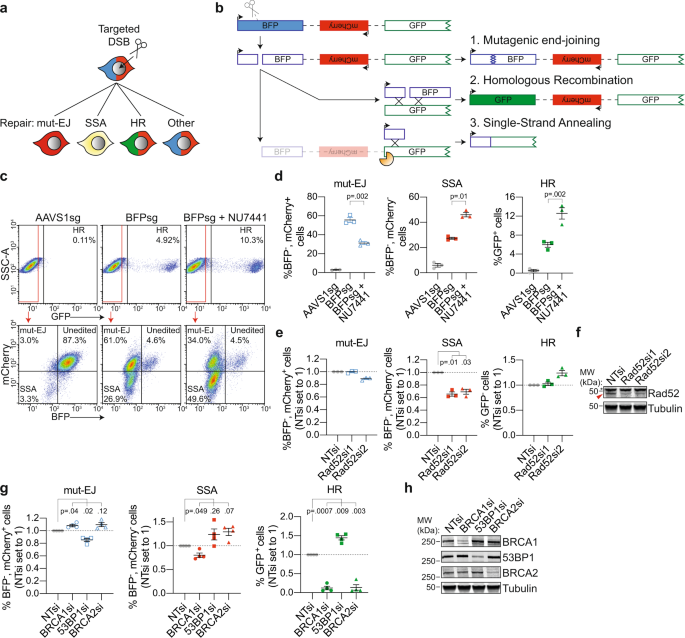
Multi-pathway DNA-repair reporters reveal competition between end-joining, single-strand annealing and homologous recombination at Cas9-induced DNA double-strand breaks | Nature Communications

H3K4 methylation at active genes mitigates transcription-replication conflicts during replication stress | Nature Communications
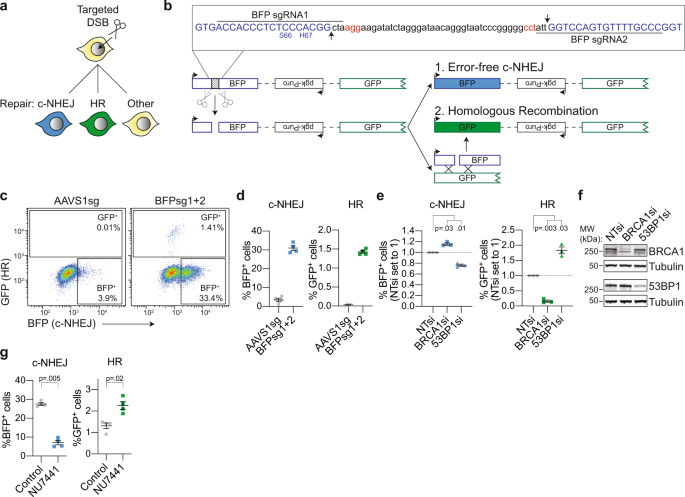
Multi-pathway DNA-repair reporters reveal competition between end-joining, single-strand annealing and homologous recombination at Cas9-induced DNA double-strand breaks | Nature Communications
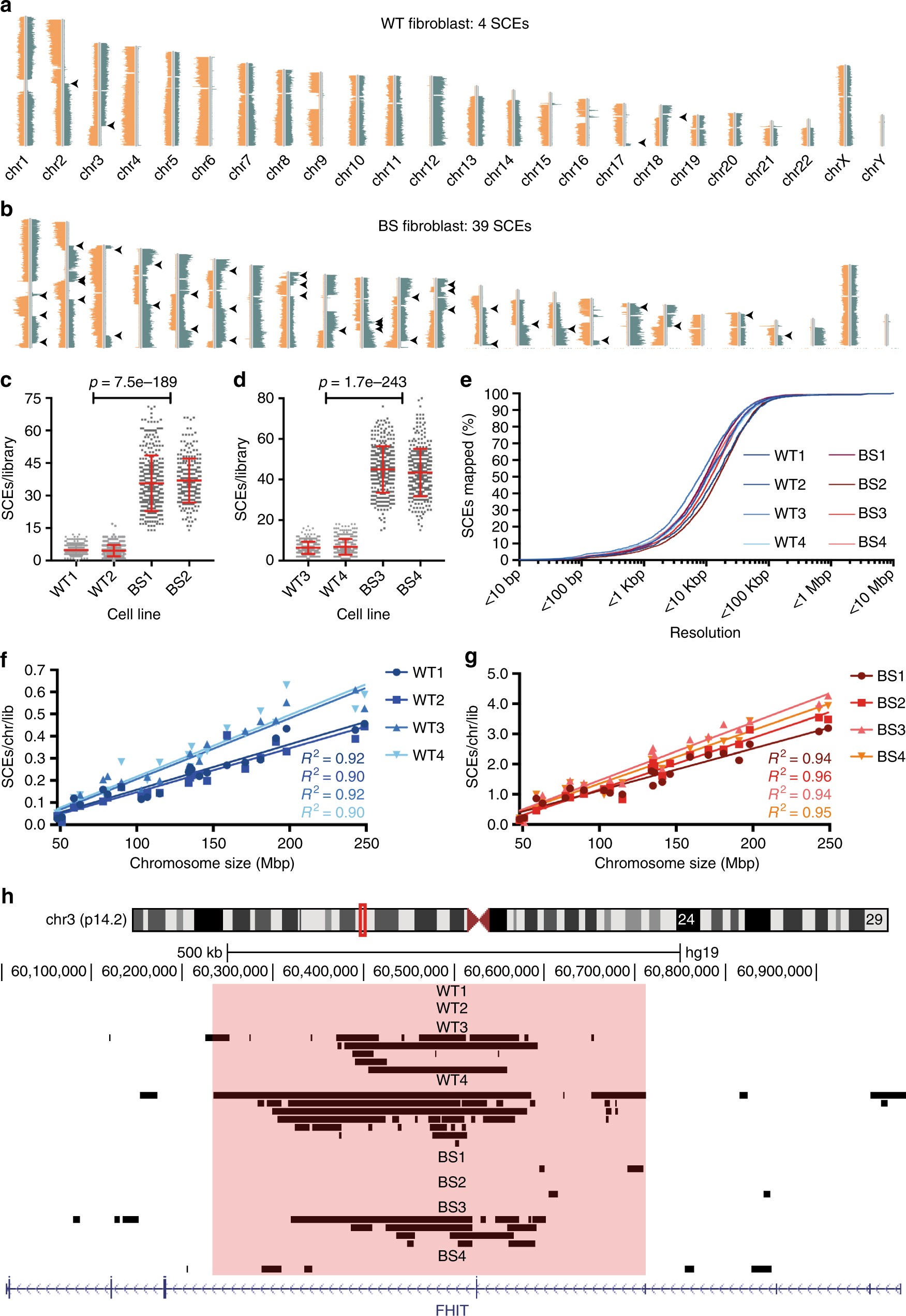
BLM helicase suppresses recombination at G-quadruplex motifs in transcribed genes | Nature Communications
Quantitative Profiling of Lysine Acetylation Reveals Dynamic Crosstalk between Receptor Tyrosine Kinases and Lysine Acetylation | PLOS ONE

Sequential Application of Anticancer Drugs Enhances Cell Death by Rewiring Apoptotic Signaling Networks: Cell
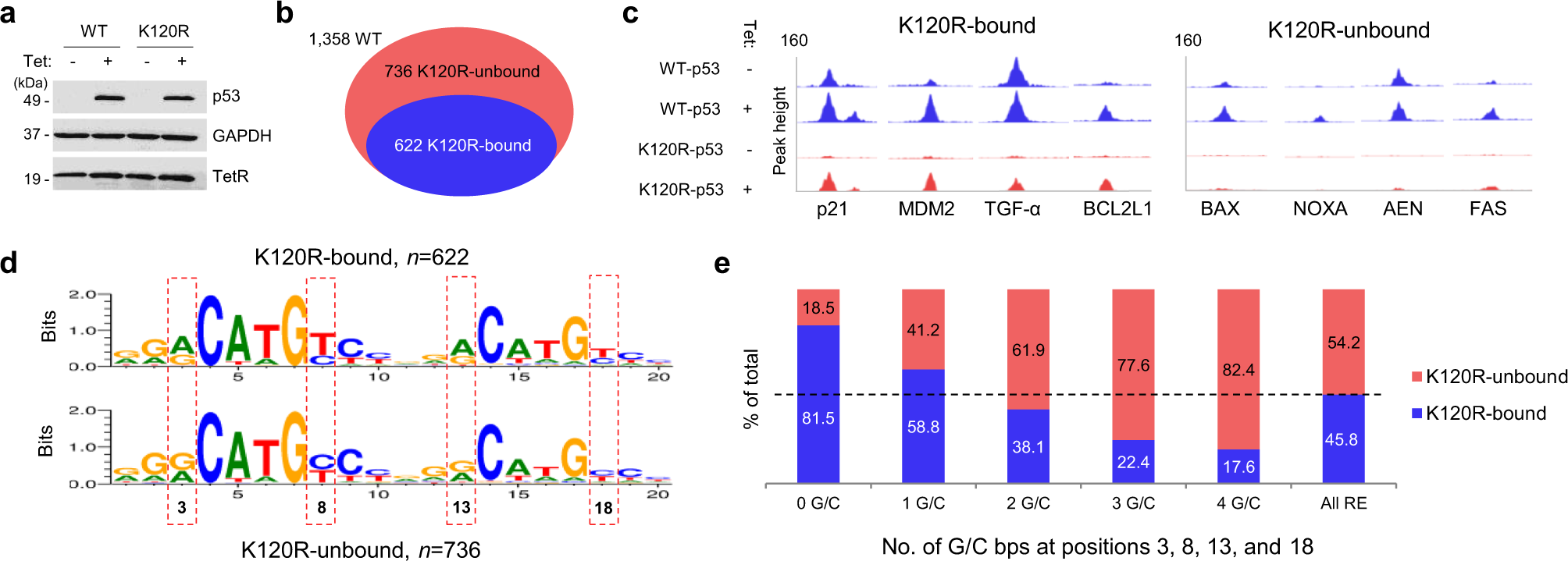
Distinct mechanisms control genome recognition by p53 at its target genes linked to different cell fates | Nature Communications

BRD4 prevents the accumulation of R-loops and protects against transcription–replication collision events and DNA damage | Nature Communications